Large-scale approaches to the pre-clinical translational study of cancer therapeutics
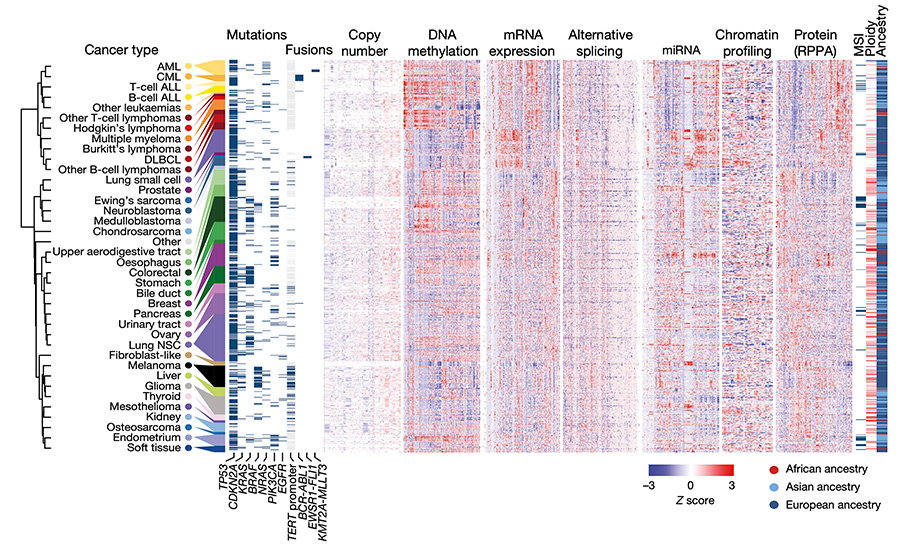 In 2005, it became clear that deep molecular annotation of cell lines and other models would be required so that models could be used in an informed manner with respect to the emerging characterizations of human cancer (e.g., TCGA).
In 2005, it became clear that deep molecular annotation of cell lines and other models would be required so that models could be used in an informed manner with respect to the emerging characterizations of human cancer (e.g., TCGA).
To this end, Bill Sellers led the Novartis-Broad team that developed the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia (CCLE).
Most recently, the CCLE team released an enhanced set of orthogonal characterizations (miRNA, methylation, RPPA, etc.) of the CCLE, including the profiling of 228 metabolites across more than 900 cell lines.
Relevant papers
Barretina J†, Caponigro G†, Stransky N, …, Sellers WR*, Schlegel R*, Garraway LA*. The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature. 2012 Mar 28;483:603-7. PMCID: PMC3320027
Gao H†, Korn JM†, Ferretti S, …, Williams JA* & Sellers WR*. High-throughput screening using patient-derived tumor xenografts to predict clinical trial drug response. Nat Medicine. 2015 Oct 19. PMID: 26479923
Li H, Ning S, Ghandi M, Kryukov GV, …, Schreiber SL, Clish CB, Garraway LA, Sellers WR. The landscape of cancer cell line metabolism. Nat Med 2019 May;25(5):850-860. PMID: 31068703
Ghandi M†, Huang FW†, Jané-Valbuena J, …, Garraway LA*, Sellers WR*. Next-generation characterization of the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. Nature. 2019 May;569:503-508 PMID: 31068700
Systematic elucidation of cancer dependencies
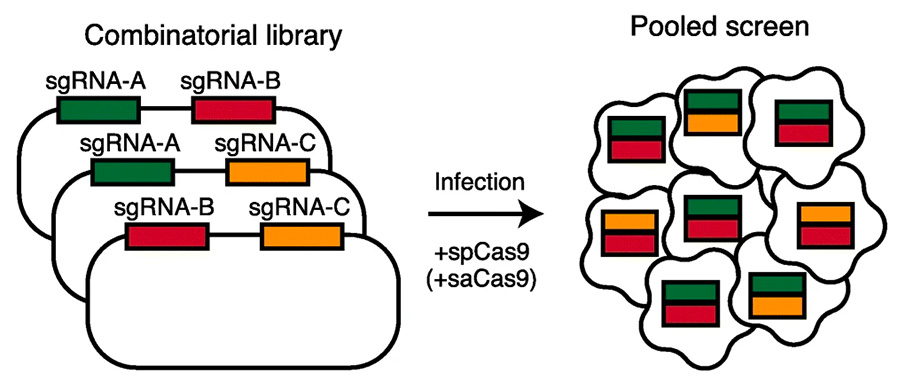 Leveraging the CCLE, within Novartis, Bill Sellers led the efforts to annotate the gene-level functional requirements for 7,700 genes targeted by an average of 20 shRNA per gene in 390+ cell lines. These efforts led to the discovery of PRMT5 as a synthetic lethal node downstream of the co-deletion of CDKN2A and MTAP. Now at the Broad Institute, our lab is focused on developing new generation combination functional genomic screens and the informatics pipelines required to process such data (see Zamanighomi M et al., below). Furthermore, we are interested in elucidating the molecular mechanisms by which cancer dependencies confer synthetic lethality.
Leveraging the CCLE, within Novartis, Bill Sellers led the efforts to annotate the gene-level functional requirements for 7,700 genes targeted by an average of 20 shRNA per gene in 390+ cell lines. These efforts led to the discovery of PRMT5 as a synthetic lethal node downstream of the co-deletion of CDKN2A and MTAP. Now at the Broad Institute, our lab is focused on developing new generation combination functional genomic screens and the informatics pipelines required to process such data (see Zamanighomi M et al., below). Furthermore, we are interested in elucidating the molecular mechanisms by which cancer dependencies confer synthetic lethality.
Relevant papers
Mavrakis KJ†, McDonald III ER†, Schlabach MR†, Billy E†, Hoffman GR†, …, Keen N, Schmelzle T, Hofmann F, Stegmeier F*, Sellers WR *. Disordered methionine metabolism in MTAP/CDKN2A-deleted cancers leads to dependence on PRMT5. Science 2016 Mar 11;351(6278):1208-13. PMID: 26912361
McDonald ER 3rd†, de Weck A†, Schlabach MR†, Billy E*, …, Hofmann F*, Schmelzle T*, Sellers WR*. Project DRIVE: A Compendium of Cancer Dependencies and Synthetic Lethal Relationships Uncovered by Large-Scale, Deep RNAi Screening. Cell. 2017 Jul 27;170(3):577-592. PMID: 28753431
Zamanighomi M†, Jain SS†, Ito T, Pal D, Daley TP, Sellers WR. GEMINI: a variational Bayesian approach to identify genetic interactions from combinatorial CRISPR screens. Genome Biol. 2019 Jul 12;20(1):137. PMID: 31300006
Ito T, Young MJ, Li R, …, Sellers WR. Paralog knockout profiling identifies DUSP4 and DUSP6 as a digenic dependence in MAPK pathway-driven cancers. Nat Genet. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-021-00967-z.
Li R, Klingbeil O, Monducci D, …, Ito T*, Sellers WR*. Comparative optimization of combinatorial CRISPR screens. Nat Commun. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30196-9.
Chang, Liang, Nancy Y. Jung, Adel Atari, Diego J. Rodriguez, Devishi Kesar, Tian-Yu Song, Matthew G. Rees, …, and William R. Sellers. 2023. “Systematic Profiling of Conditional Pathway Activation Identifies Context-Dependent Synthetic Lethalities.” Nature Genetics, September. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-023-01515-7
The development of novel cancer therapeutics
 Previously, Bill led the pre-clinical groups responsible for developing cancer therapeutics for Novartis. Multiple small molecule, antibody and cellular therapeutics were advanced into clinical trials, including therapeutics targeting PI3K, BRAF, MEK, ER, FGFR1-3, FGFR4, ABL, SHP2, IDH1, CSF1, CSF1R, PIM1-3, MET, MEK, SMO, MDM2, CDK4, DKK1, HER3, c-KIT, ALK, DR5, HSP90, HDM2 and CD19 (CART19, the first approved CAR-T therapy). To date, 7 therapeutics have achieved market approval (Encorafenib, Binimetinib, Tisagenlecleucel…).
Previously, Bill led the pre-clinical groups responsible for developing cancer therapeutics for Novartis. Multiple small molecule, antibody and cellular therapeutics were advanced into clinical trials, including therapeutics targeting PI3K, BRAF, MEK, ER, FGFR1-3, FGFR4, ABL, SHP2, IDH1, CSF1, CSF1R, PIM1-3, MET, MEK, SMO, MDM2, CDK4, DKK1, HER3, c-KIT, ALK, DR5, HSP90, HDM2 and CD19 (CART19, the first approved CAR-T therapy). To date, 7 therapeutics have achieved market approval (Encorafenib, Binimetinib, Tisagenlecleucel…).
Currently, our lab is interested in therapeutic discovery through the development and application of novel genomic, chemogenomic, proteomic and biotherapeutic tools to advance therapeutic hypotheses.
Relevant papers
Fritsch C, Huang A, Chatenay-Rivauday C, …, Sellers WR. Characterization of the novel and specific PI3Kalpha inhibitor NVP-BYL719 and development of the patient stratification strategy for clinical trials. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 May;13:1117-29. PMID: 24608574
Chen YP, LaMarche MJ, Chan H, …, Sellers WR*, Stams T*, Fortin PD*. Allosteric inhibition of SHP2 inhibits the transformed phenotype of RTK driven cancers. Nature 2016;535:148-152 PMID: 27362227
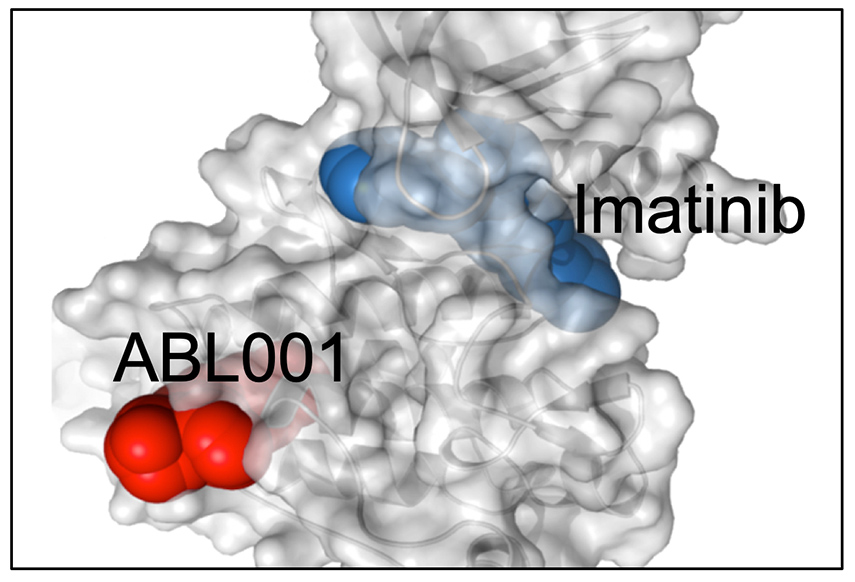
Wylie AA, Schoepfer S, Jahnke W, …, Sellers WR. The allosteric inhibitor ABL001 enables dual targeting of BCR-ABL. Nature. 2017 Mar 30;543:733-737. PMID: 28329763
Mulvaney KM, Blomquist C, Acharya N, …, Sellers WR. Molecular basis for substrate recruitment to the PRMT5 methylosome. Mol Cell. 2021 Aug; doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2021.07.019.
Huang, HT., Lumpkin, R.J., Tsai, R.W., …, Sellers. W.R. Ubiquitin-specific proximity labeling for the identification of E3 ligase substrates. Nat Chem Biol (2024). https://doi.org/10.
